|
Channel Generator:
The Channel Generator, accessible from the Channel menu in the main
dialog window, allows you to generate almost any simple sinusoidal or
linear signal. While the channel generator was mainly added to Udicus
to make debugging and testing the program easier, it could be used to
test other programs or to mimic a signal.
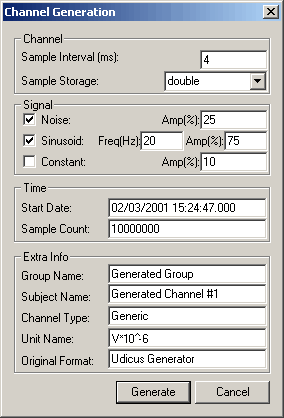 The
channel generation dialog, displayed on the left, allows you to edit
almost every detail on how a signal is stored internally in Udicus. The
channel generation dialog, displayed on the left, allows you to edit
almost every detail on how a signal is stored internally in Udicus.
Start by setting the sample interval to the desired setting: note that
the number must be written in milliseconds, and the sample rate is the
inverse of the sample interval.
The sample storage combo box allows you to choose which data type to
store your signal in. The names refer to data types as used in the C
programming language. There is a table at the bottom of this page summarizing
the features of their characteristics.
The Signal subsection of options allows you to enable the generation
of different types of signals. Noise adds pseudo-random values to each
sample, Sinusoid uses the standard sine function to create a periodic
wave of the given frequency and finally the Constant option adds the
same number to each sample. The amplitude percentages are relative to
the clipping point of the signal, so that the signal generator will
always generate a noticeable signal.
When entering the start date, you must make sure that you use the format:
dd/mm/yyyy hh:mm:ss.mmm. The end date of the signal is calculated from
the number of signals you order to generate the sample interval entered
at the top of the dialog.
The extra info set of edit boxes allow you to set the names of various
channel variables that describe the channel. The first two and the last
one should be self explanatory, but the Channel Type and the Unit Name
variable follow a specific format that must be followed (see UDCS Developer's
Manual).
Table of data types for the sample storage option:
| Name |
Size |
Can hold value of type... |
| bool |
1 bit |
true/false |
| nibble |
4 bit |
integers from 0 to 15 |
| u_char |
1 byte |
integers from 0 to 255 |
| char |
1 byte |
integers from -127 to 127 |
| u_short |
2 bytes |
integers from 0 to 65535 |
| short |
2 bytes |
integers from -32765 to 32765 |
| u_int |
4 bytes |
integers from 0 to 2^32 |
| int |
4 bytes |
integers from -2^31 to 2^31 |
| u_long |
8 bytes |
integers from 0 to 2^64 |
| long |
8 bytes |
integers from -2^63 to 2^63 |
| float |
4 bytes |
low precision decimal numbers
|
| double |
8 bytes |
high precision decimal numbers |
|